Ulcerative ColitisForest Hills, NY
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that affects the lining of the large intestine, causing inflammation and ulcers in the colon and rectum. This condition can lead to frequent bowel movements, abdominal pain, and other disruptive symptoms that interfere with daily life. While there is no known cure, many patients manage symptoms effectively with the right combination of medical treatment and lifestyle support.
Pinnacle Gastroenterology provides evaluation, diagnosis, and long-term management of ulcerative colitis. Patients experiencing gastrointestinal distress or changes in bowel habits are encouraged to seek prompt care to prevent complications and improve their quality of life. Call our office at (718) 747-9630 to learn more or schedule an appointment.
Causes of Ulcerative Colitis
The exact cause of ulcerative colitis remains unknown, though it is believed to involve an abnormal immune response. In individuals with this condition, the immune system mistakenly attacks the cells of the large intestine, leading to chronic inflammation. Environmental triggers, genetics, and gut microbiota imbalances may also contribute to disease development. According to the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation, a family history of IBD increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
Unlike other bowel diseases, ulcerative colitis is not caused by diet or stress. However, both factors can influence symptom severity. When combined with a personalized medical plan, identifying and avoiding personal triggers, such as certain foods or high-stress environments, may help reduce flare-ups.
“Environmental triggers, genetics, and gut microbiota imbalances may also contribute to disease development.”
Common Signs and Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis symptoms vary depending on the severity and location of inflammation in the colon. Some people experience mild symptoms, while others have frequent and intense flare-ups. The most common symptoms include persistent diarrhea (often with blood or pus), abdominal cramping, rectal pain, and an urgent need to defecate.
Additional symptoms may include fatigue, weight loss, fever, and, in some cases, joint pain or skin irritation. Symptoms often appear in cycles, with periods of remission followed by flare-ups. It is important to consult a gastroenterologist when symptoms are persistent or interfere with everyday activities, as untreated inflammation can lead to more serious complications such as anemia, colon damage, or an increased risk of colorectal cancer.
“The most common symptoms include persistent diarrhea (often with blood or pus), abdominal cramping, rectal pain, and an urgent need to defecate.”
How Ulcerative Colitis is Diagnosed
Diagnosing ulcerative colitis involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, lab work, and imaging. A gastroenterologist may order stool and blood tests to rule out infections and check for inflammation markers. However, a definitive diagnosis typically requires a colonoscopy with biopsy to examine the colon lining and assess the extent of the disease.
Other tests, such as CT scans or flexible sigmoidoscopy, may be used depending on the severity of symptoms. Early diagnosis is essential for managing ulcerative colitis effectively. Once a diagnosis is confirmed, the provider will determine the subtype—such as proctitis, left-sided colitis, or pancolitis—and develop a personalized treatment plan accordingly.
“A gastroenterologist may order stool and blood tests to rule out infections and check for inflammation markers.”
Treatment Options for Ulcerative Colitis
Treatment for ulcerative colitis focuses on reducing inflammation, managing symptoms, and maintaining remission. First-line therapies often include anti-inflammatory drugs such as aminosalicylates and corticosteroids. Immunosuppressive medications and biologics (e.g., infliximab or adalimumab) can also help relieve symptoms of moderate to severe cases when other options are ineffective.
For patients who do not respond to medication or who experience severe complications, surgical intervention may be necessary. A common procedure involves removing the colon and creating a new pathway for waste removal. While surgery can significantly improve quality of life, it is generally reserved for patients with severe or treatment-resistant ulcerative colitis. Regular follow-ups and lab monitoring are necessary to ensure ongoing disease control and adjust treatments as needed.
“A common procedure involves removing the colon and creating a new pathway for waste removal.”
Managing Life with Ulcerative Colitis
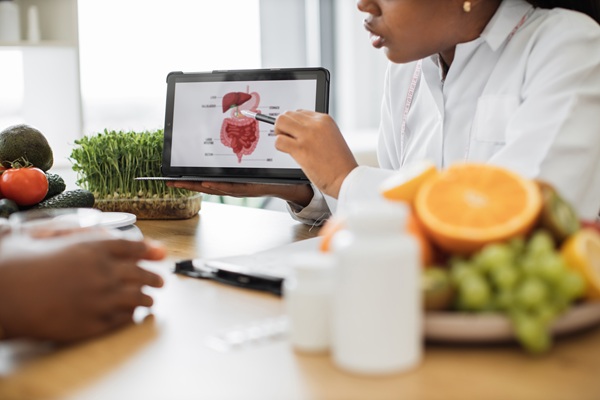
Even though ulcerative colitis is a lifelong condition, many individuals live full and active lives with proper management. Lifestyle adjustments play a key role in controlling symptoms and preventing flare-ups. We advise patients to follow a nutrient-rich, low-residue diet that reduces strain on the colon. Identifying personal food triggers—such as dairy, high-fiber foods, or spicy dishes—can help prevent discomfort.
Stress reduction techniques such as yoga, mindfulness, and regular exercise may also improve symptom management. Emotional support, whether through counseling or support groups, is often beneficial. According to the National Institutes of Health, mental health challenges such as anxiety and depression are common in IBD patients, making psychological support a valuable component of comprehensive care.
“Lifestyle adjustments play a key role in controlling symptoms and preventing flare-ups.”
Questions Answered on This Page
Q. What causes Ulcerative Colitis?
Q. What are the most common signs and symptoms of ulcerative colitis?
Q. How is Ulcerative Colitis diagnosed?
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. Can ulcerative colitis be cured?
A. There is currently no known cure for ulcerative colitis. However, many patients achieve long-term remission with medication and lifestyle changes. In cases where symptoms are severe or unmanageable with standard treatments, surgery may be necessary to remove the colon as a potential resolution for symptoms.
Q. What foods should be avoided with ulcerative colitis?
A. Food triggers vary, but common culprits include high-fiber foods, dairy products, spicy dishes, and raw vegetables during flare-ups. Keeping a food diary can help identify which items worsen symptoms. A registered dietitian or gastroenterologist can provide guidance on safe and balanced meal planning.
Q. Is ulcerative colitis the same as Crohn’s disease?
A. While both are forms of inflammatory bowel disease, ulcerative colitis affects only the colon and rectum, and inflammation is limited to the lining of the bowel. Crohn’s disease, in contrast, can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract and may involve deeper layers of the bowel wall. Each condition has distinct diagnostic and treatment considerations.
Q. What are signs of a flare-up?
A. Signs of a flare-up include increased urgency or frequency of bowel movements, bloody stools, abdominal cramping, and fatigue. Some individuals may also experience weight loss, fever, or joint pain. Flare-ups vary in intensity, and early medical intervention can help manage symptoms more effectively.
Q. How often should follow-ups occur with a gastroenterologist?
A. Patients with ulcerative colitis should have regular follow-ups, typically every 3 to 12 months, depending on disease activity and treatment response. These visits help assess medication effectiveness, monitor for complications, and make timely adjustments to the care plan. More frequent visits may be necessary during flare-ups or when starting new therapies.
Take Control of Ulcerative Colitis with Professional Care
Ulcerative colitis does not need to define your daily life. Working with a dedicated care team can lead to fewer flare-ups, more symptom-free days, and a better overall quality of life. To speak with a specialist and explore personalized options for managing ulcerative colitis, contact Pinnacle Gastroenterology today.
Our team is here to help manage chronic conditions like ulcerative colitis with a compassionate and evidence-based approach. Call us at (718) 747-9630 to schedule a consultation and begin your personalized care journey.
Contact Us
Pinnacle Gastroenterology is located at
112-03 Queens Blvd Ste 204
Forest Hills,
NY 11375